Using Python
Create the basics programs
Let's create the program for our small automation setup using two Niryo robots.
We'll build what is commonly referred to as a coordinated dual-robot system. While the term "Master-Slave" is often used, in this case, it's more accurate to say one robot triggers actions on the second robot, rather than fully controlling it. Each robot executes its own program independently, but their actions are synchronized using digital inputs and outputs.
Step 1: Create the master robot program
Connect to your first robot(which will act as the "master", the one with the conveyor belt connected) and create a new Python program.
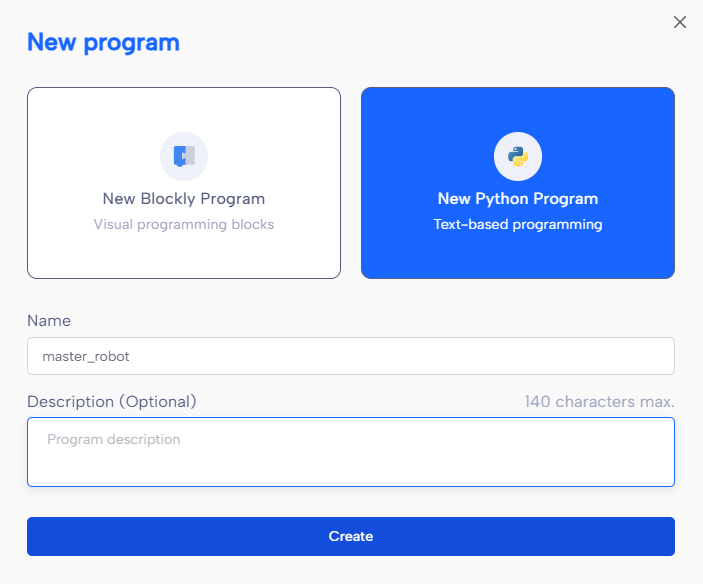
First, since we use pyniryo , we need to specify the ip_adress of the robot. You can find it in by clicking on the top left corner and checking the current connected robot :
and checking the current connected robot : 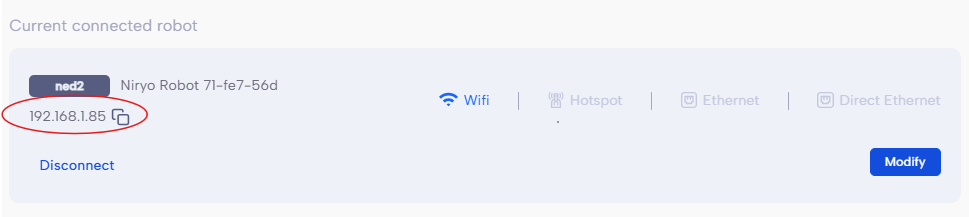
In my case the ip_adress is "192.168.1.85"
from pyniryo import *
robot_ip_address = "IP ADRESS TO CHANGE" ex: "192.168.1.79"
robot = NiryoRobot(robot_ip_address)
robot.calibrate_auto()
robot.update_tool()
robot.set_conveyor()Then, create the core logic of your program. Here, we will perform a simple pick and place operation : picking an object from a ramp and placing it on a conveyor.
robot.run_conveyor(ConveyorID.ID_1, speed=100, direction=ConveyorDirection.BACKWARD)
robot.digital_write('DO1', PinState.LOW)
while True:
# ensure tool ready to pick
robot.release_with_tool()
# Home position
robot.move(JointsPosition(-0.001, 0.499, -1.251, -0.001, -0.008, -0.003))
while robot.digital_read('DI1') == PinState.HIGH:
robot.wait(1)
robot.digital_write('DO1', PinState.HIGH)
# Intermediate position
robot.move(JointsPosition(-1.017, 0.066, -0.475, -0.146, -1.324, -0.006))
# Approach position to the ramp
robot.move(JointsPosition(-0.981, -0.472, -0.42, -0.463, -1.042, -0.003))
# pick on the ramp
robot.move(JointsPosition(-1.022, -0.507, -0.475, -0.408, -0.878, -0.003))
robot.grasp_with_tool()
robot.move(JointsPosition(-0.981, -0.472, -0.42, -0.463, -1.042, -0.003))
robot.digital_write('DO1', PinState.LOW)
# approach to the conveyor
robot.move(JointsPosition(0.238, -0.208, -0.781, 0.06, -0.595, -0.008))
# Place on the conveyor
robot.move(JointsPosition(0.24, -0.332, -0.804, 0.049, -0.448, -0.009))
robot.release_with_tool()
💡 You can already test this program to validate that the first robot performs its actions correctly!
Step 2: Create the slave robot program
Now, connect to the second robot and create a new Python program.
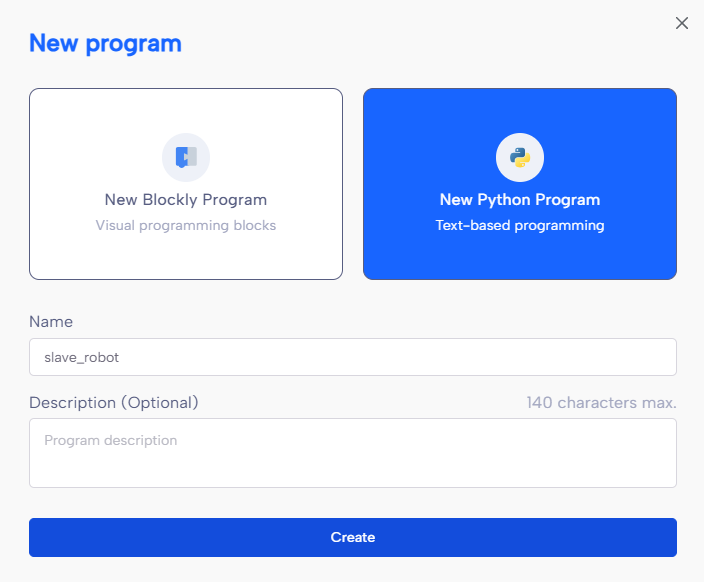
Here is the code for the slave robot :
# !/usr/bin/env python3
from pyniryo import *
robot_ip_address_2 = "IP ADRESS TO CHANGE" ex : "192.168.1.80"
robot2 = NiryoRobot(robot_ip_address_2)
robot2.calibrate_auto()
robot2.update_tool()
# ensure tool ready to pick
robot2.release_with_tool()
# Home position
robot2.move(JointsPosition(-0.001, 0.499, -1.251, 0, -0.002, 0.002))
# Approach conveyor
robot2.move(JointsPosition(-0.301, -0.076, -0.808, 0.06, -0.672, 0.46))
# pick conveyor
robot2.move(JointsPosition(-0.288, -0.167, -0.816, 0.042, -0.629, 0.468))
robot2.grasp_with_tool()
robot2.move(JointsPosition(-0.301, -0.076, -0.808, 0.06, -0.672, 0.46))
# Intermediate position
robot2.move(JointsPosition(0.433, 0.327, -0.736, 0.18, -1.315, 0.072))
# Approach Top of the ramp
robot2.move(JointsPosition(1.635, 0.252, -0.681, 0.482, -1.121, 1.45))
# Place on the ramp
robot2.move(JointsPosition(1.681, 0.189, -0.763, 0.525, -0.982, 1.353))
robot2.release_with_tool()
# Home position
robot2.move(JointsPosition(-0.001, 0.499, -1.251, 0, -0.002, 0.002))
In this program, we end by returning the robot to its Home position. This is important to free up the ramp area, which is shared between the two robots.
🛠 In the next steps, we'll connect both robots using digital I/O so they can communicate and coordinate their actions seamlessly.


