Vision
Kurse mit 'Vision' markiert
Spiele Tic Tac Toe
- Content Type: Tutorial
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Ned2
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: In diesem Kurs sind noch keine Teilnehmer/innen eingeschrieben.
Visuelle Kommissionierung mit Künstlicher Intelligenz unter Verwendung von TensorFlow
- Content Type: Tutorial
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Ned2
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: In diesem Kurs sind noch keine Teilnehmer/innen eingeschrieben.
Einführung in Robotik, Blockprogrammierung und Automatisierung
- Length: 35h
- Content Type: Curriculum
- Programming: Blockly
- Equipment: Bundle discovery
Entdecke die Welt der Robotik mit unserem umfassenden Lehrplan, der für Studierende und Lehrkräfte entwickelt wurde, die die Grundlagen der Automatisierung, Programmierung und robotischen Anwendungen erforschen möchten. Dieser Kurs führt die Teilnehmenden von der Geschichte der Robotik bis hin zur praktischen Programmierung und industriellen Automatisierung mit dem kollaborativen Roboter NED2 (Cobot) und der Blockly-Programmierung.
Für wen ist dieser Kurs geeignet?
✔️ Studierende in MINT- oder technischen Ausbildungsprogrammen
✔️ Lehrkräfte, die einen strukturierten Robotik-Lehrplan suchen
✔️ Einsteiger:innen, die Robotik und Automatisierung ohne Programmierkenntnisse lernen möchten
✔️ Alle, die sich für industrielle Robotik und Automatisierung interessieren
Melde dich noch heute an und mach den ersten Schritt zum Profi in Robotik und Automatisierung! 🚀
- Trainer/in: Malcom Niryo
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 125
Add-on ROS2 : Enhance your simulated Niryo Robot for Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance
- Content Type: Add-on
- Programming: ROS2
- Equipment: Ned2 + Vision Set
This ROS2 add-on adds obstacle avoidance capabilities to the simulated Niryo NED2 robot. Using Gazebo and ROS2, you’ll learn how to simulate dynamic environments and make the robot navigate safely around obstacles. The add-on focuses on integrating basic sensors, processing environmental data, and implementing reactive behaviors. It’s a practical extension for testing navigation logic and improving robot autonomy in complex settings. Let’s make your robot smarter in simulation.
This course provides a structured and hands-on approach to advanced simulation and manipulation using ROS2 and Gazebo Sim. Throughout the course, you will learn to:
-
Create an engineering plan to solve a robotics problem efficiently.
-
Simulate depth cameras and distance sensors in Gazebo Sim for realistic environment interaction.
-
Work with SDF and URDF files to define and adjust robot and environment models.
-
Understand and use ROS2 messages for inter-node communication.
-
Establish communication between ROS2 and Gazebo Sim to synchronize simulation and control.
-
Use the Octomap plugin with MoveIt2 to generate 3D maps and support motion planning.
-
Create and manage YAML parameter files for modular and reusable configuration.
-
Develop a test strategy to validate functionalities and ensure system robustness.
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 59
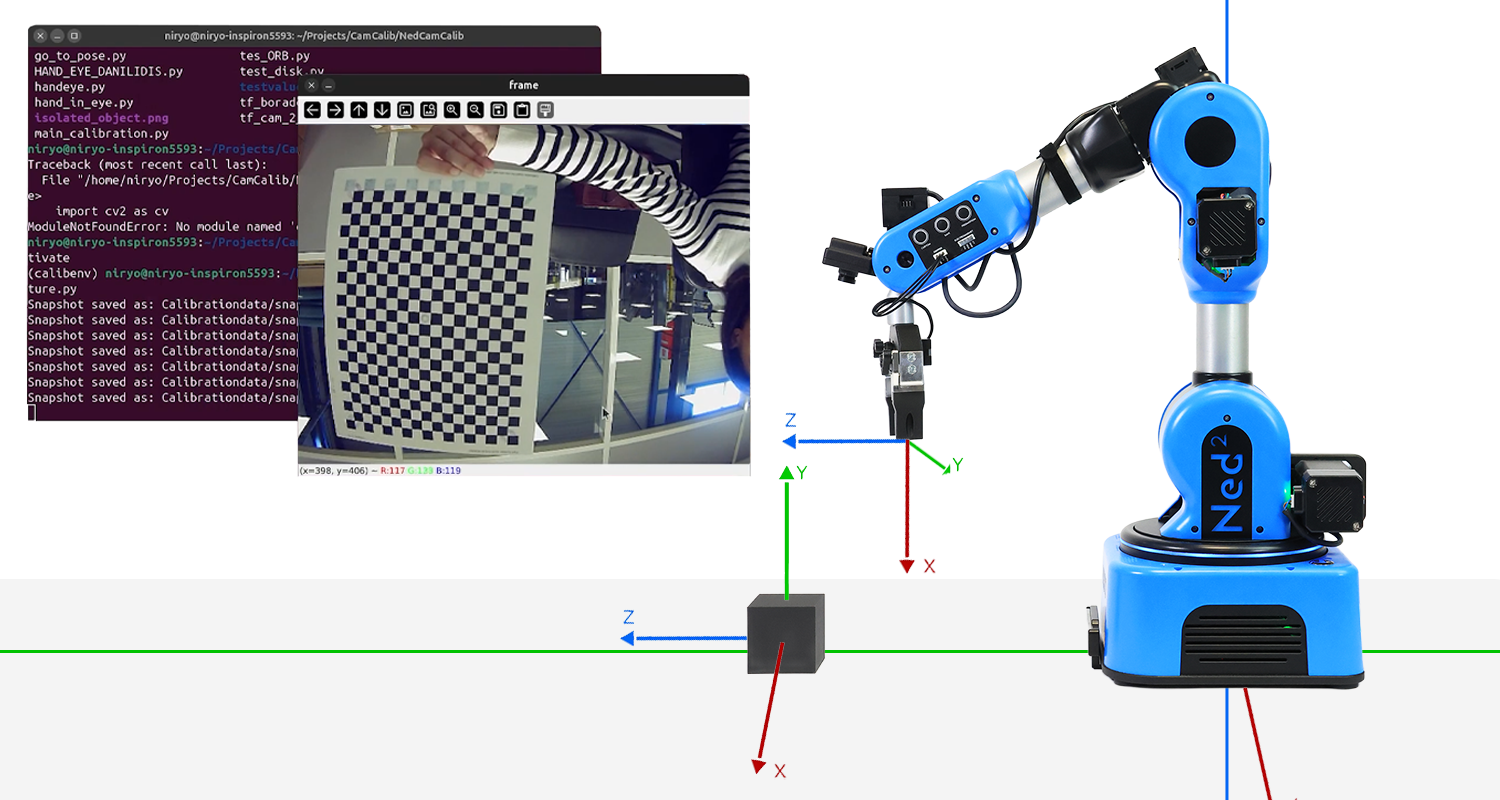
Vision Pipeline: From Camera to Grasping with the Niryo Ned2
- Length: 16h
- Content Type: Lab
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Ned2
Can a robot truly understand what it sees?
This hands-on lab takes you on a journey from raw images to precise robotic actions. Using only a single camera mounted on the Niryo Ned2, you will build a full perception, pipeline from camera calibration to object detection and real-time grasp execution.
The current vision system relies on a monocular camera mounted on the robot's wrist and a calibrated workspace using visual markers (tags). Here are the technical specifications of this onboard camera:
- Sensor type: IMX322 (CMOS)
- Resolution: 640 × 480
- Pixel size: 12.8 × 11.6 μm
- Field of view (FOV): approximately 104°
- Focal length: approximately 3 mm
This setup, while functional, presents several technical and methodological limitations:
- Need for visual tags to guide the robot.
- Demanding workspace configuration that must remain fixed and precisely calibrated.
- High sensitivity to errors, whether from robot movements or setup changes.
- Vulnerability to lighting conditions, shadows, or reflections.
- Detection limited to a few predefined rigid objects.
When a human looks at an object, they can estimate its position, distance, and orientation almost instinctively. Our brains have been trained since birth to perceive depth, interpret shadows, relative sizes, movements, and reconcile information from both eyes. It’s a rich, complex, yet entirely transparent process for us.
A camera, however, doesn’t see like a human. It captures only a 2D projection of a 3D world. It has no sense of depth or understanding of the scene’s context. Estimating an object’s pose (its position and orientation in space) from a single image is therefore a fundamentally ambiguous and ill-posed task.
This is compounded by several challenges specific to the industrial context of this project:
- Exclusive use of a monocular camera, without direct access to depth.
- Camera is mobile, as it is mounted on the robot, making localization difficult.
- No additional sensors (stereo, LIDAR, etc.).
- Camera noise, lighting, resolution.
In response to these challenges, the goal of this lab is to build a robust, reliable, and coherent image processing pipeline in which the only source of information is a monocular onboard camera—and the end goal is to guide a robotic arm to interact correctly with one or more objects in its environment.
The lab thus aims to design a system that:
- Operates without a preconfigured workspace or visual tags,
- Adapts to a mobile, onboard camera,
- Enables flexible recognition of a wide range of objects using their CAD models,
- Provides 6D pose estimation (position + orientation) in the robot's base frame,
- Detects multiple objects simultaneously with dynamic selection,
- Remains robust to environmental variations.
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 85
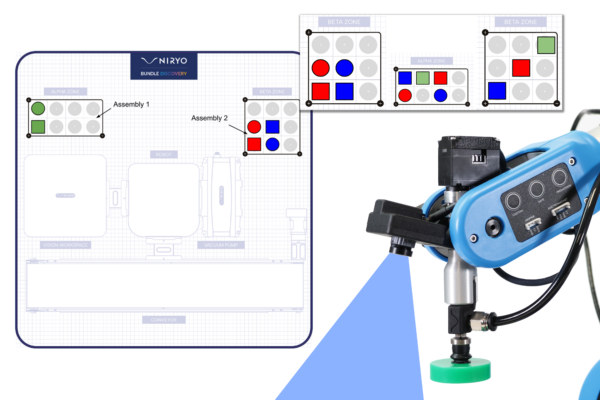
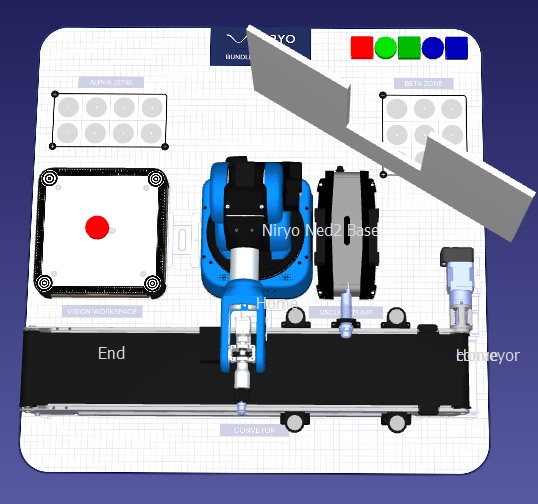
Bundle Discovery: Montage und Auftragsvorbereitung
- Length: 6h
- Content Type: Lab
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Bundle discovery
Szenario
Wir möchten eine Montage durchführen, bei der bestimmte manipulierbare Objekte (Form und Farbe) in den Zonen ALPHA und BETA nach einem vom Benutzer definierten Muster angeordnet werden. Um diese Montage durchzuführen, werden die manipulierbaren Objekte dem Roboterarm NED2 über ein Förderband zugeführt. Der Roboterarm NED2 identifiziert dann die Teile, bevor er sie aufnimmt. Wenn das aufgenommene manipulierbare Objekt nicht für das Muster benötigt wird, wird es im Abfallbereich (Ausschuss) abgelegt, andernfalls wird es in den Zonen ALPHA oder BETA entsprechend dem gegebenen Muster platziert.

Inhalt des Labors
Kapitel 1: Pick and Place
- Definition von Referenzpunkten und Interessenspunkten im Arbeitsbereich des Roboterarms NED2.
- Erstellung der Bewegungsabfolge für eine Pick-and-Place-Operation.
- Durchführung einer Palettier-Operation.
Kapitel 2: Definition eines Musters
- Erstellung einer Eingabefunktion für den Bediener und einer Mustererstellungsfunktion.
- Bestimmung, ob ein manipulierbares Objekt zu einem bestehenden Muster gehört.
- Auslösung der entsprechenden Aktion für ein manipulierbares Objekt gemäß den folgenden Fällen: gehört nicht zu einem Muster, gehört zu einem Muster und wurde bereits verarbeitet, gehört zu einem Muster und wurde noch nicht verarbeitet.
Kapitel 3: Vision
- Zuführung des manipulierbaren Objekts über das Förderband.
- Beherrschung der Ergebnisse der Kameradetektion: Form, Farbe und Position eines manipulierbaren Objekts in einem definierten Arbeitsbereich.
- Aufnahme eines von der Kamera identifizierten manipulierbaren Objekts.
Kapitel 4: Integration
- Automatische Erstellung eines vom Bediener eingegebenen Musters unter Verwendung der vom Förderband gelieferten manipulierbaren Objekte.
Vorausgesetztes Wissen
Python: Grundsyntax + einfache Daten- und Kontrollstrukturen + Schleifen + einfache Funktionsaufrufe
Benötigte Komponenten
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 89
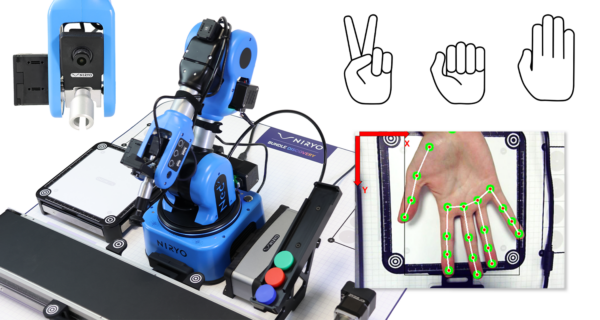
Die Erkundung der KI-gesteuerten Zusammenarbeit in der Robotik
- Length: 8h
- Content Type: Lab
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Bundle discovery
Szenario
Das Szenario ermöglicht die Interaktion zwischen einem Bediener und dem Roboterarm NED2, mithilfe von Schnittstellen, die auf künstlicher Intelligenz basieren. Insbesondere kann der Bediener durch Gesten das Teil auswählen, das vom Roboterarm NED2 aufgenommen werden soll – jede Geste entspricht dabei einem Teil aus einer in der Alpha-Zone angeordneten Sammlung. Der Roboterarm NED2 legt das gegriffene Teil in die Hand des Bedieners, nachdem er mithilfe der Vision-Set-Kamera die Position oberhalb der Ladezone identifiziert hat. Dies ist eine Pick-and-Place-Sequenz, bei der die Aufnahme- und Ablagepunkte in Echtzeit durch die Gestenbefehle des Bedieners vorgegeben werden. Die Erkennung der Gesten und der Handposition erfolgt mit Deep-Learning-Werkzeugen.
Das Ziel des Szenarios besteht darin, diesen Vorgang anhand der im folgenden Algorithmus dargestellten Schritte auszuführen:
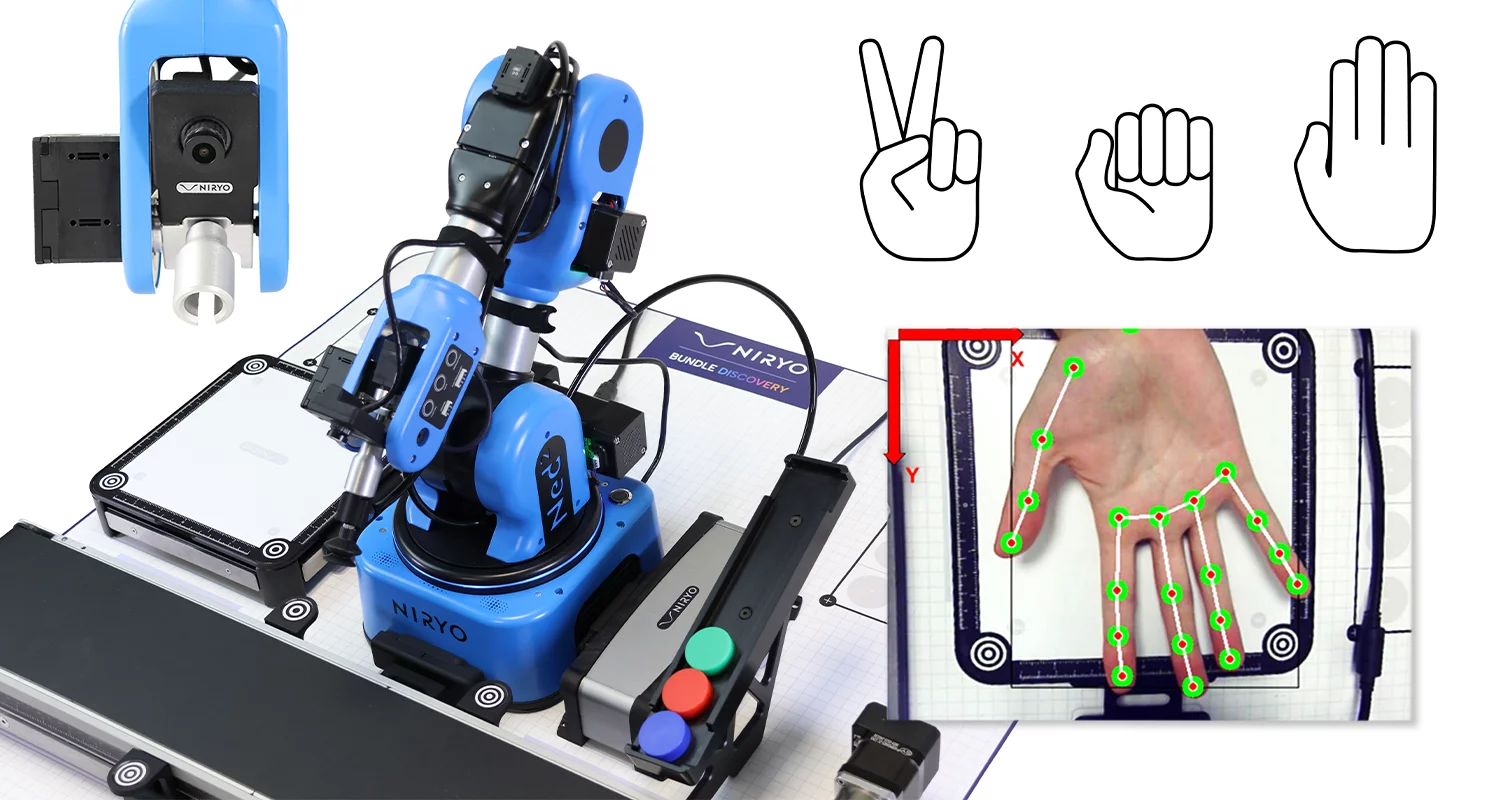
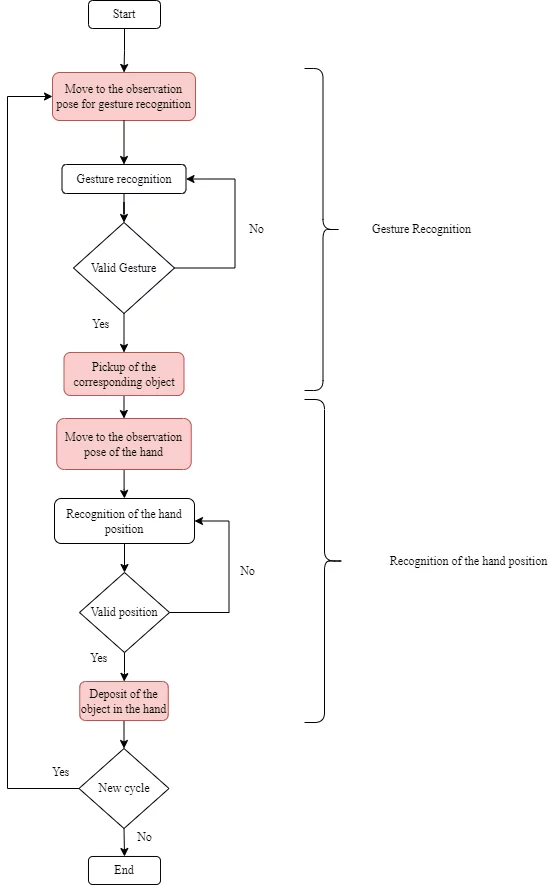
Inhalt des Labors
Kapitel 1: Pick and Place
- Interessante Punkte definieren
- Bewegungen für Pick and Place erstellen
Kapitel 2: Gestenerkennung
- Verwendung von Teachable Machine zum Trainieren eines Modells erlernen
- Vorhersagen auf Grundlage von Gesten erhalten
- Einen Filter erstellen, um eine Geste zu validieren
Kapitel 3: Handerkennung
- Die Hand im Kamerabild erkennen
- Die Kamera kalibrieren
- Die Koordinaten des Ablagepunkts in der Mitte der Hand bestimmen
Kapitel 4: Integration
- Die Teilprogramme in ein komplexes und funktionales Programm integrieren
Vorkenntnisse
Python: Grundlegende Syntax + einfache Daten- und Kontrollstrukturen + Schleifen + einfache Funktionsaufrufe
Bezugssysteme und Transformationen: Verstehen, wie kartesische Koordinatensysteme funktionieren und das Prinzip von Transformationen
Erforderliche Ausstattung





- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 89
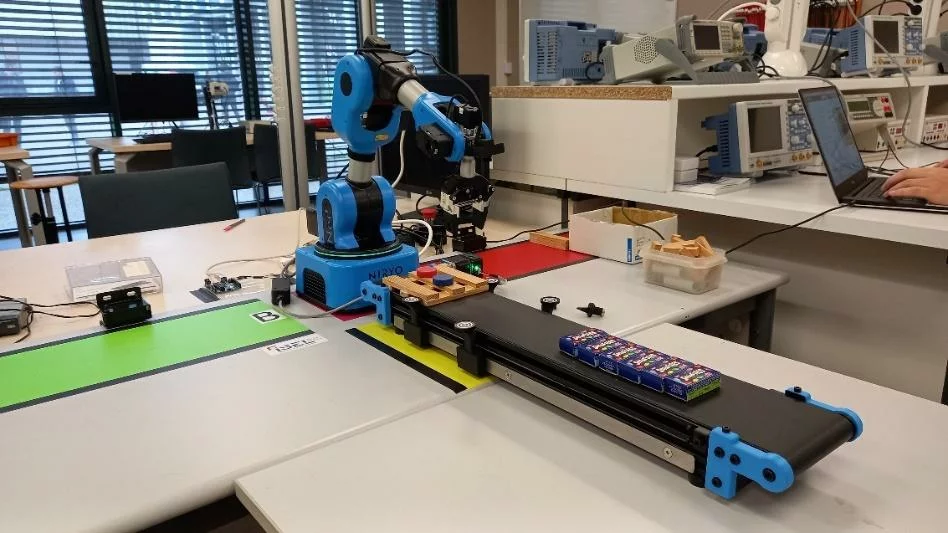
CNC Machine Tool Loading and Unloading
- Length: 8h
- Content Type: Lab
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Bundle discovery
We want to create a loading and unloading scenario for a machine tool. The robotic arm NED2 will have to coordinate with a virtual machine tool to enable a part to be loaded into the machine, machined, unloaded onto the conveyor and then cleared from the area by the conveyor. The machine tool will simulate machining and cleaning cycles in a loop, and the robotic arm NED2 will act in coordination.
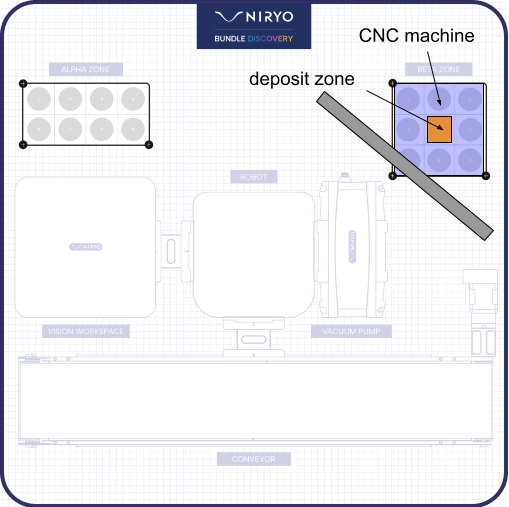
Laboratory Contents
Chapter 1: Pick and place
- Practice the notions of reference points and points, associated with a tool and a base, in robotics.
- Understand and master articular and linear movement sequences.
- Perform pick-and-place operations in a workspace using a specific tool.
Chapter 2: Vision
- Understand and control an RGB camera's settings in a specific environment.
- Put into practice object detection with the camera.
Chapter 3: Generating trajectories
- Create the virtual environment of a robotic cell using robotic simulation software.
- Simulate a trajectory to check its feasibility and extract the information needed to program a robot.
- Compare robotic arm NED2 trajectories with simulation and optimize.
Chapter 4: Synchronization with a PLC
- Integrate operator controls into the robotic arm NED2’s environment.
- Be able to simulate robotic arm NED2’s operations with on-screen displays to develop complex behaviors.
- Deepen your programming knowledge with thread implementation in Python.
- Apply the synchronization of the robotic arm NED2's movements with external commands.
- Learn how to define the main stages of a machine tool loading and unloading operation.
Chapter 5: Integration
- Be able to create partial integrations constituting sub-systems.
- Be able to integrate all subsystems.
Prerequisite knowledge
Python: Basic syntax + simple data and control structures + loops + simple function calls
Required components





- Trainer/in: Pauline Vanpoulle
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 89
Sorting of merchandise under the supervision of a Web server
- Length: 6h
- Content Type: Lab
- Programming: Python
- Equipment: Bundle STEM
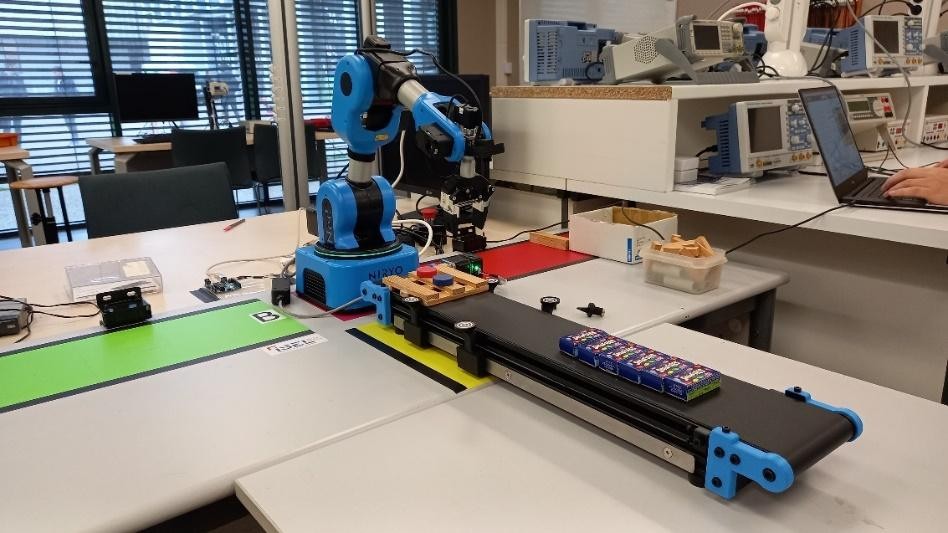
The objective of the Lab is to reproduce a robotic operation of sorting goods and palletizing in a logistics warehouse under the supervision of a web server (figure 1). The goods (red and green pucks) are placed randomly by an operator and transported by the conveyor. Arriving in the gripping zone (figure 2), the conveyor stops and the goods (red and green pucks) are located and identified by the camera placed at the end of the manipulator arm. The two-finger gripper, mounted at the end of the arm, grabs the puck and places it according to its color, on a pallet in zone A (red) or zone B (green) for delivery to two different destinations.
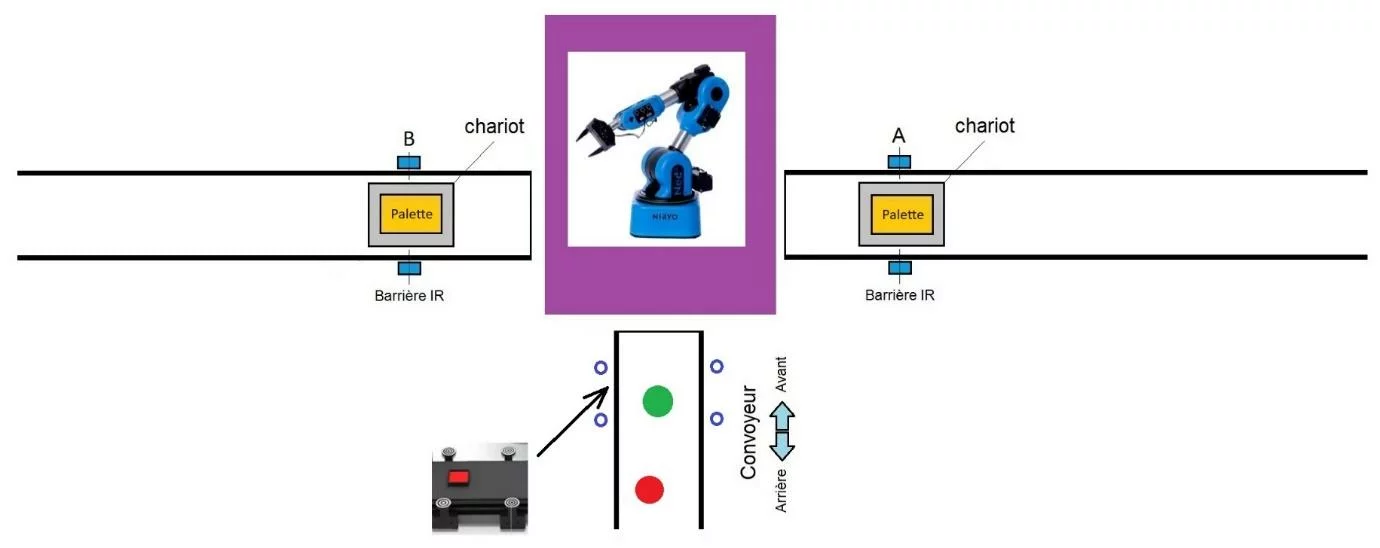
Lab Content
Chapter 1: Server Setup
- Understand the existing links between the Python code and the WEB page
Chapter 2: Controlling the conveyor
- Implementing the Python commands to control the conveyor
Chapter 3: Pick and Place using Vision
- Master the sequence of movements necessary to pick up a part by vision and place it in the dedicated area, without colliding with the environment
Chapter 4: Database
- Develop skills in manipulating databases with Python, and interacting with a user interface to view and export data
Required Equipment




Prerequisite knowledge
Programming :
- Basic notions of algorithms and the Python language
- Using Databases in Python
- Linux commands (if needed)
Networks & Communication :
- Networking Basics
Setup
Software to install:
- NyrioStudio
- Python 3
- Flask, Sqlite3
- Eingeschriebene Teilnehmer/innen: 88